How you store your cryptocurrency affects everything from security protocols to how quickly and easily you can access your funds. It also dictates whether you’re the one in full control of your digital assets.
Two primary storage options are custodial and non-custodial wallets. Custodial wallets rely on a trusted third party to manage private keys, while non-custodial wallets put full ownership in your hands—along with the responsibility of securing your private keys and executing transactions.
Whether you're a retail investor, institutional trader, or cryptocurrency enthusiast, choosing between them depends on your priorities. Some prefer the convenience and security of third-party management. Others value self-custody and full ownership of their assets.
Both custodial and non-custodial wallets have their place, depending on your risk tolerance and technical expertise.
Key Takeaways:
-
Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, offering built-in security, backups, and ease of use.
-
Non-custodial wallets give users complete control over their private keys. With that control comes the responsibility of managing security and backups.
-
Security and recovery options differ significantly between the two, shaping how users protect and access their assets.
-
Choosing between custodial vs. non-custodial wallets depends on what matters most—convenience, security, regulatory alignment, or full autonomy.
At a Glance: Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial and non-custodial crypto wallets each offer distinct trade-offs between security, control, and convenience. One entrusts a third party to safeguard assets, while the other puts you fully in charge. Here’s how they compare:
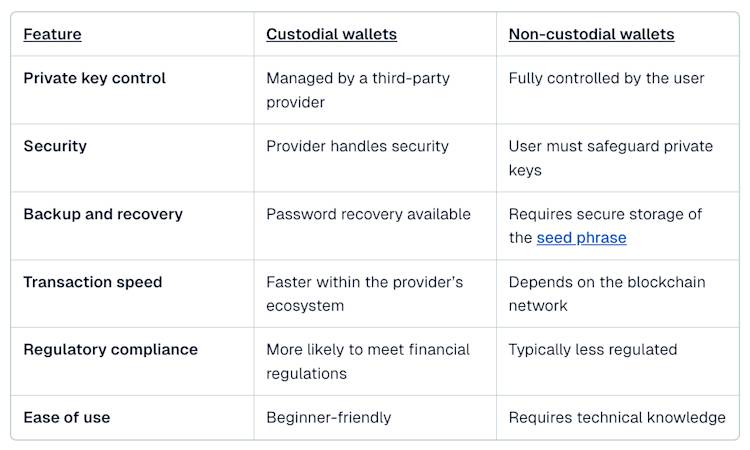
As you can see, the management of custodial and non-custodial wallets comes down to control. Custodial wallets simplify security, recovery, and compliance but require trust in a third party. Non-custodial wallets put you in charge, offering full autonomy with the responsibility of securing your assets. The right choice depends on your priorities.
What Is a Custodial Wallet?
A custodial wallet is a cryptocurrency wallet in which a third party—such as an exchange or custody provider—holds and manages private keys on the user’s behalf. Instead of direct control, users trust the custodian to secure their assets.
Centralized exchanges, financial institutions, and specialized crypto custody providers commonly offer custodial wallets. They’re attractive to investors who prioritize ease of use and professional security measures.
Since private keys are managed externally, users can access funds through a platform login, similar to online banking. Recovery options, like email verification and customer support, help restore access if you lose your credentials.
Custodians enhance security through multi-signature authentication (multi-sig), cold storage (offline key storage that prevents unauthorized access), and strict regulatory compliance.
While custodial wallets simplify security and reduce personal responsibility, they require trust in the provider’s protocols, stability, and compliance standards.
Pros and Cons
Custodial wallets come with trade-offs in terms of control and reliance on a third party. Here’s a breakdown of the drawbacks and benefits of using a custodial wallet.
Pros
-
Ease of use: No need to manage private keys, making them ideal for beginners and institutional investors.
-
Backup and recovery: Customer support can restore lost credentials, reducing the risk of permanent asset loss.
-
Institutional-grade security: Protection against hacks, fraud, and unauthorized access through encryption and multi-sig authentication.
-
Regulatory compliance: Many custodians follow financial regulations, adding credibility and legal protections for users.
-
Customer support: Dedicated assistance is generally available for account issues, transaction disputes, and security concerns.
Cons
-
Lack of full control: Users rely on the provider for access to funds, which can limit financial autonomy.
-
Potential withdrawal restrictions: Some custodial wallets enforce withdrawal limits, delays, or transaction approvals.
-
Risk of provider breaches: If the custodian is compromised or goes bankrupt, user funds could be at risk of loss or seizure.
-
Regulatory exposure: Government regulations, freezing policies, and compliance requirements may impact fund accessibility.
Use Cases
Custodial wallets are popular among:
-
New investors and beginners, who may prefer user-friendly platforms that eliminate the need for private key management.
-
Traders and active investors, who might value custodial wallets’ faster transactions and higher liquidity within centralized ecosystems.
-
Businesses and crypto payment providers prioritizing security and regulatory compliance that help pave the way for safe transactions and adherence to financial standards.
-
Institutions seeking secure crypto storage solutions to safeguard assets without the complexities of self-management.
What Is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
A non-custodial wallet (also known as a decentralized wallet) gives users complete control over their private keys. In other words, they are the sole custodians of their assets. Unlike custodial wallets, no third party holds or manages the funds. Non-custodial wallets are a decentralized storage solution that aligns with the original core philosophy of the crypto movement—self-sovereignty and trustless transactions.
When setting up a wallet, users generate private and public keys, along with a 12- to 24-word seed phrase that serves as the recovery method. Users directly authorize transactions, meaning they’re in complete control.
Since non-custodial wallet funds aren’t stored on exchanges, they remain safe from exchange breaches, but security is entirely the user’s responsibility. Losing the seed phrases means losing access permanently.
Non-custodial wallets come in multiple forms, including hardware wallets, non-custodial hot wallets, and browser-based wallets. Non-custodial hot wallets, such as mobile and desktop wallets, offer accessibility but require extra security precautions as they remain online.
Pros and Cons
Unlike custodial solutions that provide backup and recovery options, non-custodial wallets require users to manage their own security, which can be both an advantage and a risk. Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits and trade-offs:
Pros
-
Full control: Users own their private keys and assets, eliminating reliance on third parties.
-
Stronger security: No exposure to exchange hacks, custodial failures, or regulatory freezes.
-
Increased privacy: Transactions remain independent of centralized oversight, reducing exposure to surveillance and data tracking.
-
No withdrawal limits: Users can move funds freely anytime without restrictions or delays imposed by service providers.
Cons
-
No recovery support: Losing private keys results in a permanent loss of assets.
-
Higher technical burden: Users must manage private keys, wallet security, and backups.
-
Potential for human error: Incorrect transactions can’t be reversed, such as if funds are sent to the wrong address.
Use Cases
Non-custodial wallets are commonly used by:
-
People comfortable managing private keys who want complete control over their assets.
-
Long-term investors who prioritize security over convenience and want to protect their holdings from third-party risks.
-
Privacy-conscious users seeking the autonomy to keep their transactions independent of centralized oversight.
-
NFT collectors and Web3 enthusiasts who use them to engage with decentralized apps while maintaining full ownership of their digital assets.
Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Crypto Wallets: Which to Choose
Choosing between custodial and non-custodial wallets depends on your security needs, experience level, and how much control you want over your assets.
Custodial wallets are ideal for users who prefer a managed approach, where a trusted provider handles security, backups, and recovery. This makes them a convenient option for institutions, enterprises, and new investors who want reliable access to their funds without the risk of losing private keys.
Non-custodial wallets offer complete autonomy, giving users control of their private keys and transactions. While they provide greater privacy and independence, they require users to manage the security of their assets.
For businesses and investors looking to efficiently manage custodial and non-custodial wallets, BitGo offers comprehensive solutions tailored to different security and compliance needs. Whether you need institutional-grade protection or a self-custody option that keeps you in control, BitGo’s wallet solutions ensure your digital assets are secure and accessible.
FAQ
Why would someone choose a non-custodial wallet?
Non-custodial wallets give users complete control over their private keys and funds. They provide greater privacy, eliminate reliance on third parties, and allow direct access to decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. However, they also require users to secure their keys and manage backups.
What are the potential risks of using a custodial wallet?
The main risk of a custodial wallet is that users don’t control their private keys, meaning access to funds depends on the security and stability of the provider. If the custodian experiences a security breach or imposes withdrawal restrictions, users could face delays or loss of funds.
How do custodial wallets differ from non-custodial wallets in security?
Custodial wallets rely on institutional security measures such as multi-signature authentication, cold storage, and regulatory compliance to protect assets. Non-custodial wallets put security in the user’s hands, requiring them to safeguard their private keys and protect against phishing attacks and hardware failures.
In short, custodial wallets offer professional-grade protection but introduce counterparty risk. Non-custodial wallets eliminate reliance on a third party but demand strict self-management.
Can I convert assets easily between custodial and non-custodial wallets?
Yes, you can transfer assets between custodial and non-custodial wallets simply by sending the crypto from one wallet to another. However, you may face network fees, processing times, and potential withdrawal limits from custodial services. Some providers, including BitGo, offer a solution for managing both wallet types within a single platform.
Table of Contents
- At a Glance: Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
- What Is a Custodial Wallet?
- Pros and Cons
- Use Cases
- What Is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
- Pros and Cons
- Cons
- Use Cases
- Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Crypto Wallets: Which to Choose
- FAQ
- Why would someone choose a non-custodial wallet?
- What are the potential risks of using a custodial wallet?
- How do custodial wallets differ from non-custodial wallets in security?
- Can I convert assets easily between custodial and non-custodial wallets?
The latest
All NewsAbout BitGo
BitGo is the leading infrastructure provider of digital asset solutions, delivering custody, wallets, staking, trading, financing, and settlement services from regulated cold storage. Since our founding in 2013, we have focused on enabling our clients to securely navigate the digital asset space. With a large global presence through multiple regulated entities, BitGo serves thousands of institutions, including many of the industry's top brands, exchanges, and platforms, as well as millions of retail investors worldwide. As the operational backbone of the digital economy, BitGo handles a significant portion of Bitcoin network transactions and is the largest independent digital asset custodian, and staking provider, in the world. For more information, visit www.bitgo.com.
©2025 BitGo Inc. (collectively with its affiliates and subsidiaries, “BitGo”). All rights reserved. BitGo Trust Company, Inc., BitGo Inc., and BitGo Prime LLC are separately operated, wholly-owned subsidiaries of BitGo Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation headquartered in Palo Alto, CA. No legal, tax, investment, or other advice is provided by any BitGo entity. Please consult your legal/tax/investment professional for questions about your specific circumstances. Digital asset holdings involve a high degree of risk, and can fluctuate greatly on any given day. Accordingly, your digital asset holdings may be subject to large swings in value and may even become worthless. The information provided herein is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person or entity in any jurisdiction or country where such distribution or use would be contrary to law or regulation. BitGo is not directing this information to any person in any jurisdiction where the publication or availability of the information is prohibited, by reason of that person’s citizenship, residence or otherwise.




